For this reason, the American government cut NASA’s budget. And many future missions that were planned for the new few years, like Apollo 20, were cancelled. That’s why the Apollo 13 mission came at a crucial time in the history of space travel. NASA had to prove to the American government that it was still worth spending money on space. That’s why the primary mission objective of Apollo 13 was not only to inspect and survey the moon’s soil but to also develop the human capability to work in the moon’s environment.
The design of Apollo 13’s spacecraft was similar to that of the previous space missions. Mainly, there were four main components Command module, service module, lunar module, and launch escape system.
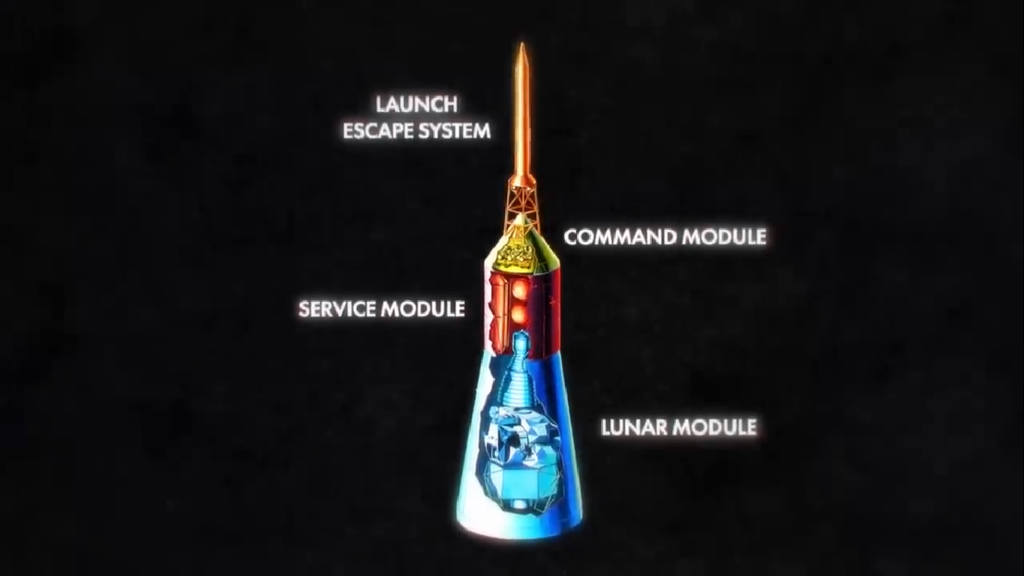
The spacecraft was launched on a Saturn V rocket. All three astronauts were seated in the command module, which was the main part of the spacecraft. But it was a small part. The command module is just this cone shape which is only 11 feet long and has a diameter of 13 feet.
All the instrument panels, navigation gear, radios, life support system, and small engines were all in this command module. The second most important part was the service module, which had most of the oxygen for the astronauts. It had some more engines too and fuel cells to generate electricity. The command and service module is often collectively called the Command And Service mModule or CSM in short form.
They are connected during the entire mission until the astronauts return to Earth. And only during the re-entry to Earth are they separated from each other.