NATO’s Southern and Eastern Borders : NATO, or the North Atlantic Treaty Organization, is a military alliance that plays a crucial role in maintaining peace and security among its member countries. Understanding why NATO’s southern and eastern borders are important requires looking at the various challenges and opportunities these regions present. Both borders face unique threats, but they are also interconnected in many ways. This article will explore the significance of these borders in global politics and security.
Historical Context of NATO
NATO was founded in 1949 as a response to the threat posed by the Soviet Union during the Cold War. Its primary purpose was to ensure collective defense, meaning that an attack on one member would be considered an attack on all. Over the years, NATO has expanded its membership and adapted its strategies to address new challenges, including terrorism, cyber threats, and geopolitical tensions.
Importance of NATO’s Eastern Border
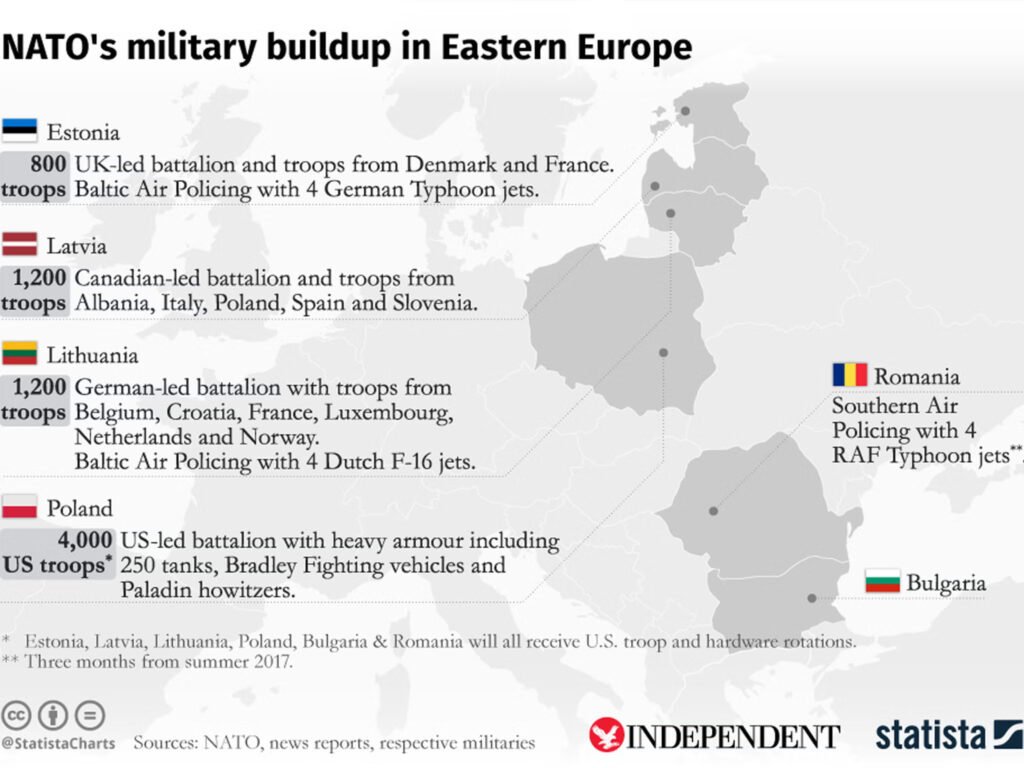
- Geopolitical Tensions with Russia: The eastern border of NATO includes countries like Poland, Latvia, Lithuania, and Estonia. These nations share a border with Russia, which has shown aggressive behavior in recent years, such as the annexation of Crimea in 2014 and ongoing military actions in Ukraine. This behavior poses a direct threat to NATO members in Eastern Europe.
- Collective Defense Strategy: The presence of NATO forces in Eastern Europe serves as a deterrent against potential Russian aggression. By deploying multinational battlegroups in these countries, NATO demonstrates its commitment to collective defense and reassures member states of their security.
- Military Exercises and Readiness: NATO conducts regular military exercises in Eastern Europe to enhance readiness and interoperability among member forces. These exercises help prepare for potential conflicts and strengthen alliances within the region.
- Support for Ukraine: The situation in Ukraine has highlighted the importance of NATO’s eastern border. While Ukraine is not a NATO member, the alliance has provided support through training, equipment, and political backing to help Ukraine defend itself against Russian aggression.
- Energy Security: Many Eastern European countries rely on energy supplies from Russia. NATO’s presence can help secure energy routes and diversify energy sources for these nations, reducing their vulnerability to potential cut-offs by Russia.
Importance of NATO’s Southern Border
- Terrorism and Instability: The southern border of NATO includes countries along the Mediterranean Sea and extends into North Africa and the Middle East. This region faces significant challenges related to terrorism, political instability, and civil wars. Groups like ISIS have exploited these conditions, posing threats not only to regional security but also to Europe.
- Migration Pressures: Instability in the southern neighborhood has led to increased migration toward Europe. Conflicts in countries like Syria and Libya have created large numbers of refugees seeking safety in European nations. NATO’s involvement can help manage these migration flows through partnerships with affected countries.
- Strategic Partnerships: NATO has been working to strengthen partnerships with countries in the southern Mediterranean region through initiatives like the Mediterranean Dialogue and the Istanbul Cooperation Initiative. These partnerships aim to address shared security concerns such as terrorism, organized crime, and illegal immigration.
- Climate Change Impacts: Climate change is exacerbating existing challenges in southern regions by causing food insecurity, water scarcity, and natural disasters. These issues can lead to further instability and conflict. NATO must consider climate change as part of its strategic planning for southern borders.
- Economic Opportunities: The southern border is also important for economic reasons. It is a crossroads for global trade routes connecting Europe with Africa and Asia. Strengthening security in this region can facilitate trade and economic development.
Interconnectedness of Southern and Eastern Borders
While NATO’s southern and eastern borders face different challenges, they are interconnected:
- Shared Threats: Both borders experience threats from non-state actors such as terrorist groups that can operate across regions. For instance, instability in North Africa can lead to increased migration pressures on Europe’s southern border while also affecting security dynamics in Eastern Europe.
- Geopolitical Competition: The influence of countries like Russia and China extends into both regions. Russia’s military presence in Libya and its support for various groups in Africa illustrate how its actions can impact both NATO’s southern and eastern flanks.
- Holistic Security Approach: Recognizing the interconnected nature of these borders is crucial for developing effective strategies. A comprehensive approach that addresses threats from both sides can enhance overall security for NATO members.
- Cooperation Among Allies: Strengthening cooperation between eastern and southern members can lead to better resource sharing, intelligence exchange, and joint operations against common threats.
Future Directions for NATO
As global politics continue to evolve, so too must NATO’s strategies regarding its southern and eastern borders:
- Enhanced Defense Posture: Continued investment in military capabilities along both borders is essential for deterrence against potential aggressors while ensuring readiness for various types of conflicts.
- Strengthening Partnerships: Building stronger relationships with non-NATO countries in both regions will be vital for addressing shared security concerns effectively.
- Focus on Stability: Initiatives aimed at stabilizing regions affected by conflict or political unrest should be prioritized to prevent spillover effects that could threaten European security.
- Adaptation to New Threats: As new challenges emerge—such as cyber warfare or climate-related issues—NATO must adapt its strategies accordingly to remain effective.
- Promoting Democratic Values: Supporting democratic governance in neighboring regions can help create a more stable environment that reduces threats emanating from authoritarian regimes.
Also Read : NATO’s Southern and Eastern Borders
Conclusion
NATO’s southern and eastern borders are crucial for maintaining peace and security not just within Europe but globally as well. The interconnected nature of threats faced by these regions highlights the need for a comprehensive approach that addresses both traditional military concerns and emerging challenges like terrorism and climate change.By strengthening its presence along these borders, enhancing partnerships with neighboring countries, and adapting strategies to meet evolving threats, NATO can continue to play a vital role in ensuring stability for its member states and promoting global security in an increasingly complex world.
FAQs
1. What are NATO’s southern and eastern borders?
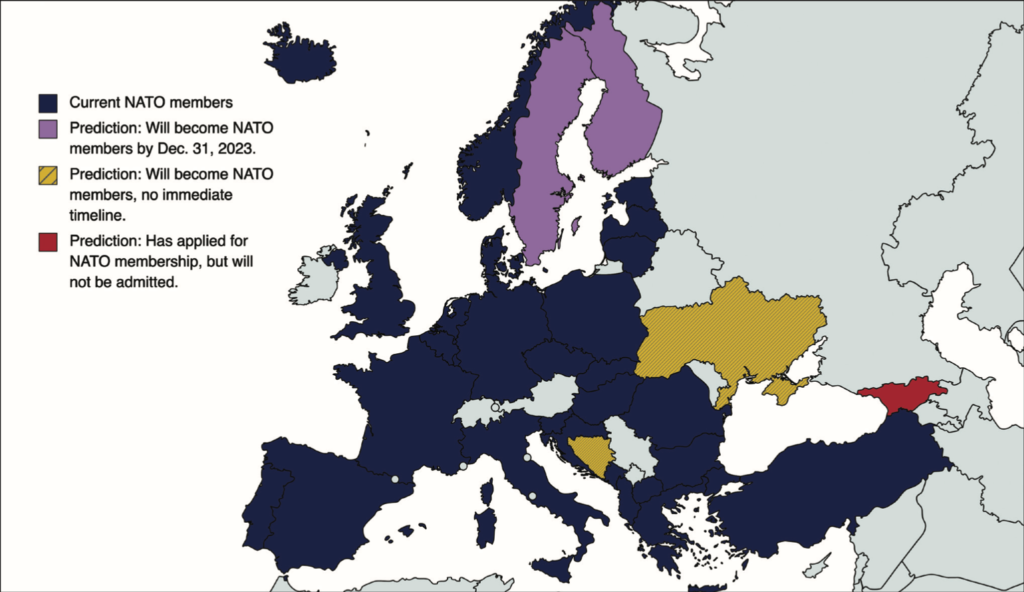
NATO’s southern border includes countries along the Mediterranean Sea, North Africa, and the Middle East. The eastern border consists of member countries like Poland, Latvia, Lithuania, and Estonia, which share borders with Russia.
2. Why is the eastern border important?
The eastern border is crucial because it faces direct threats from Russia. The aggressive actions of Russia, such as the annexation of Crimea and military involvement in Ukraine, pose significant security concerns for NATO members in this region.
3. How does NATO support its eastern members?
NATO supports its eastern members by deploying multinational battlegroups in countries like Poland and the Baltic states. This presence acts as a deterrent against potential Russian aggression and reassures these nations of their security.
4. What challenges does NATO face on its southern border?
NATO’s southern border faces challenges such as terrorism, political instability, and migration pressures from conflicts in countries like Syria and Libya. These issues can lead to increased violence and instability in Europe.
5. How does NATO address threats from terrorism in the south?
NATO addresses terrorism by enhancing cooperation with partner countries in the southern region. This includes counterterrorism training and assistance to help improve security and stability.
6. Why is migration a concern for NATO’s southern border?
Migration is a concern because instability in the southern neighborhood leads to large numbers of refugees seeking safety in Europe. NATO must manage these migration flows to maintain security.
7. How are the southern and eastern borders interconnected?
The southern and eastern borders are interconnected because threats from one region can affect the other. For example, instability in North Africa can lead to increased migration pressures on Europe’s southern border while also impacting security dynamics in Eastern Europe.